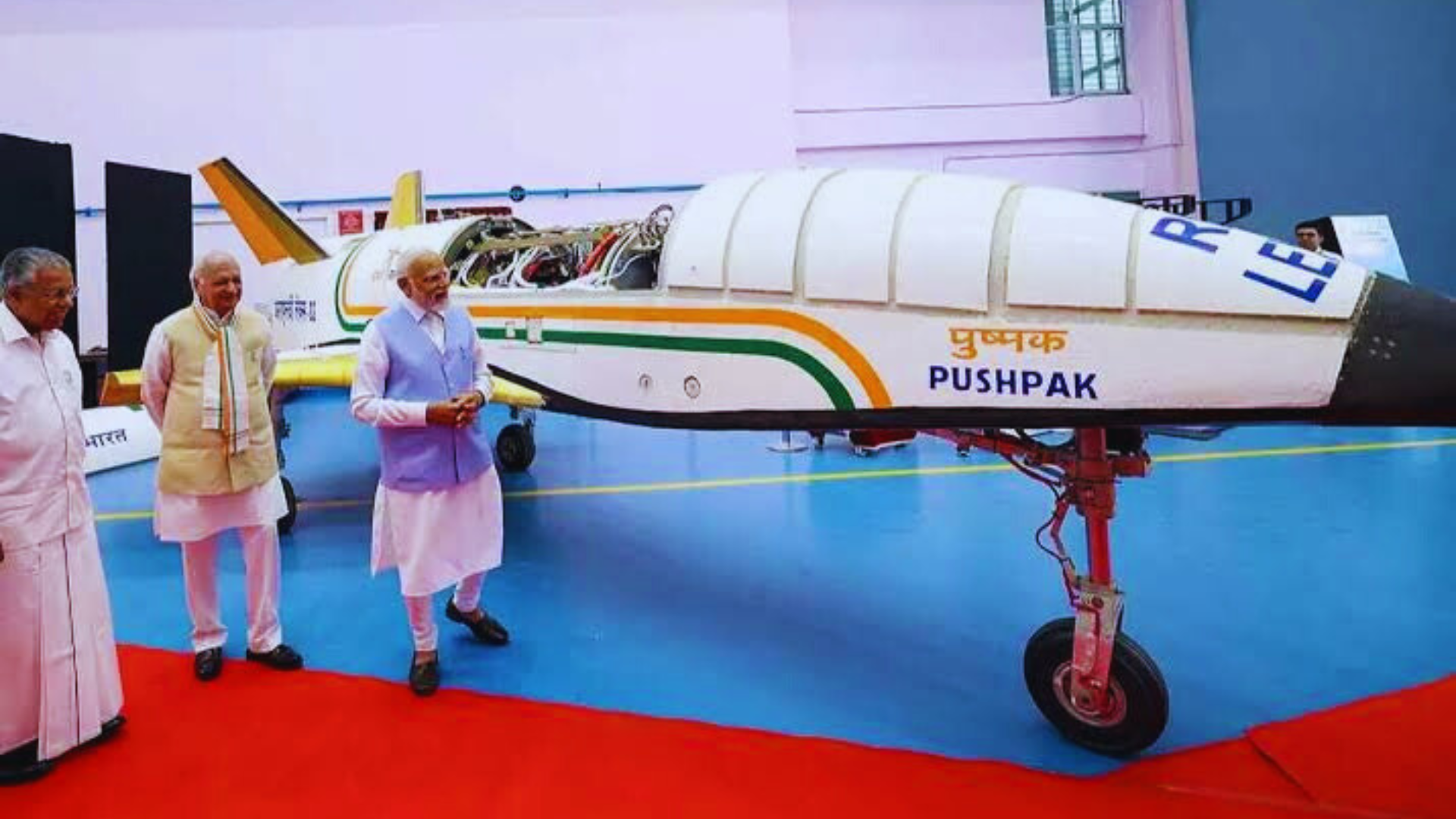
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) achieved another significant milestone as it successfully landed its Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) named ‘Pushpak’ from the Aeronautical Test Range (ATR) in Karnataka’s Challakere. This marks the second successful landing in the series of experiments conducted at the Aeronautical Test Range in Chitradurga, Karnataka.
RLV-LEX-02 Experiment:
🇮🇳ISRO nails it again!🎯
Pushpak (RLV-TD), the winged vehicle, landed autonomously with precision on the runway after being released from an off-nominal position.
🚁@IAF_MCC pic.twitter.com/IHNoSOUdRx
Advertisement · Scroll to continue— ISRO (@isro) March 22, 2024
The rocket was launched at around 7 am from the Chalakere Runway, making it the third landing mission of the RLV. Named after the legendary spaceship in the Ramayana, Pushpak, ISRO had previously conducted successful missions in 2016 and April last year.
The launch vehicle was carried to an altitude of about 4.5 km by an Indian Air Force helicopter and released after attaining predetermined parameters.
ISRO’s mission aims at developing essential technologies for a fully reusable launch vehicle to enable low-cost access to space. ISRO Chairperson S Somanath highlighted that the Pushpak launch vehicle is India’s ambitious endeavor to make access to space more affordable. It features a reusable upper stage, aiming to minimize space debris and reduce costs associated with satellite launches.
The Pushpak RLV is designed as an all-rocket, fully reusable single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) vehicle, incorporating advanced technology demonstrators. It consists of a fuselage, nose cap, double delta wings, twin vertical tails, and active control surfaces such as Elevons and Rudder.
ISRO envisions the Pushpak RLV to play a crucial role in the future of space exploration, including refueling of in-orbit satellites and refurbishment missions. The mission was briefed to Prime Minister Narendra Modi during his visit to the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre in Trivandrum in February.