The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has recently unveiled a comprehensive set of 17 dietary guidelines aimed at promoting healthier eating habits among Indians. The guidelines, developed in collaboration with the National Institute of Nutrition (NIN), emphasize the importance of a balanced and diverse diet coupled with healthy lifestyle practices.
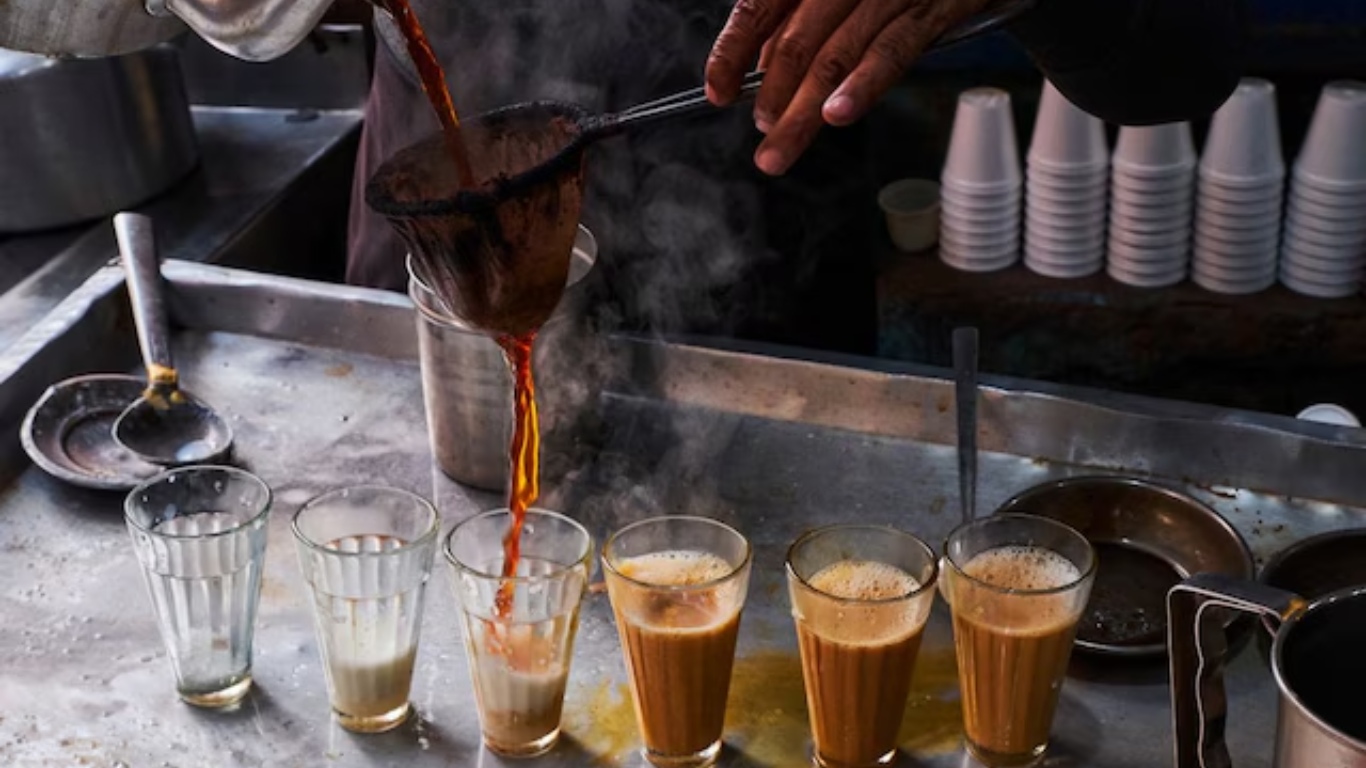
One notable recommendation from the ICMR urges moderation in the consumption of tea and coffee, popular hot beverages deeply ingrained in Indian culture. While acknowledging the cultural significance and widespread consumption of these beverages, the medical panel cautioned against excessive intake, citing potential health risks associated with caffeine.
“Tea and coffee contain caffeine, which stimulates the central nervous system and induces physiological dependence,” explained the ICMR researchers, underscoring the need for moderation in consumption to avoid exceeding tolerable limits of caffeine intake.
Providing insight into the caffeine content of commonly consumed variants, the guidelines highlighted that a cup (150ml) of brewed coffee contains 80–120mg of caffeine, instant coffee contains 50–65mg, and tea contains 30–65mg of caffeine. To ensure responsible consumption, the ICMR recommended adhering to a daily limit of 300mg of caffeine.
Also read: PM Modi Expected to Secure Massive Victory in Varanasi, Says PMK Leader Anbumani Ramadoss
Furthermore, the guidelines advised against consuming tea or coffee at least one hour before and after meals due to the presence of tannins, compounds known to interfere with iron absorption in the body. Tannins can bind to iron in the digestive tract, inhibiting its absorption and potentially leading to iron deficiency, a condition associated with anaemia and other health complications.
Highlighting the importance of iron in physiological processes such as oxygen transport and energy production, the ICMR underscored the need for adequate iron intake to maintain overall health and vitality.
Moreover, the guidelines shed light on the potential health benefits of consuming tea without milk, including improved blood circulation and reduced risk of conditions such as coronary artery disease (CAD) and stomach cancer. However, excessive consumption of coffee was cautioned against, as it has been linked to high blood pressure and cardiac irregularities.
In addition to recommendations regarding tea and coffee consumption, the dietary guidelines advocated for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and seafood while limiting oil, sugar, and salt intake. The panel discouraged the use of protein supplements, emphasizing the importance of obtaining essential nutrients from natural food sources.
By promoting balanced dietary habits and lifestyle choices, the ICMR aims to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being, laying the foundation for a healthier and more resilient population.