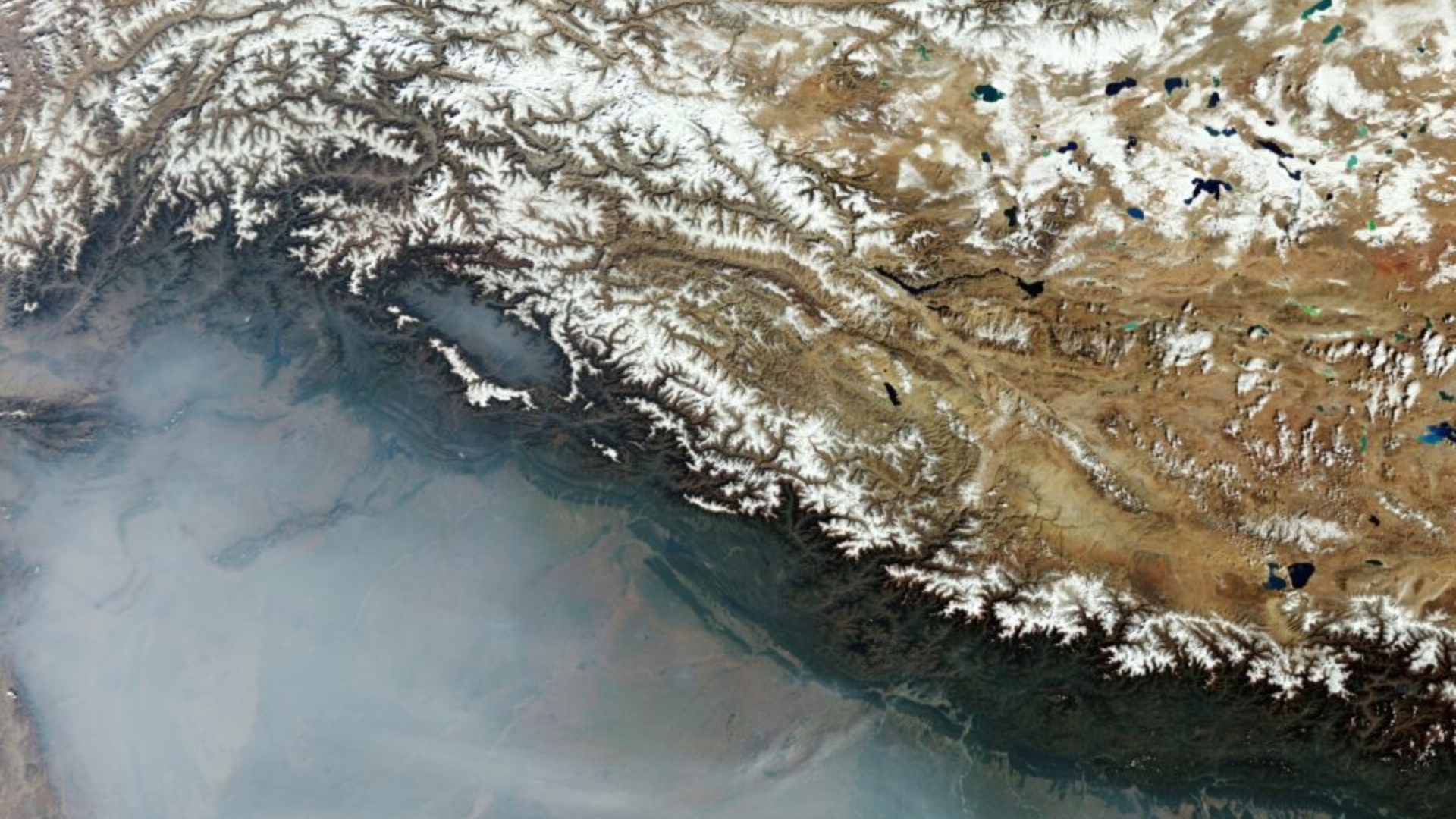
The European Space Agency’s Image of the Day showcases the plains of Northern India and Pakistan enveloped in haze and smoke.
ESA noted, “The haze is attributed to the plains being more humid than the mountainous areas dominating the upper part of the image. Smoke significantly contributes to the white veil, stemming from paddy stubble burning. This practice, common in the Indian regions of Punjab and Haryana, involves burning crop remnants at the season’s end to prepare for the next growing season.”
The Northern Indian plains, nestled at the base of the Himalayas, form part of the expansive Indo-Gangetic Plain, renowned for its fertility and dense population. This area, particularly in the foothills, is referred to as the Terai-Bhabar region in India, spanning Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Bihar, and West Bengal, and extending into Nepal.
The Bhabar strip, a narrow land belt at the Himalayan foothills, features rocky, porous soil, dense forests, and wild streams. Acting as a natural filtration system, it sees streams vanish underground, reemerging in the Terai zone.
The Terai zone, situated just south of the Bhabar, boasts marshy land and swamps, renowned for its fertile, alluvial soil, making it ideal for agriculture.
Characterized by a subtropical climate, the region experiences hot summers, monsoon rains, and mild winters.