As the U.S. approaches a pivotal election, the influence of minority voters has never been more crucial. With candidates like Vice President Kamala Harris and former President Donald Trump vying for support, their strategies and appeals to various demographic groups are paramount. This article examines the shifting dynamics among Latino, Asian-American, and Black voters and the implications for both candidates.
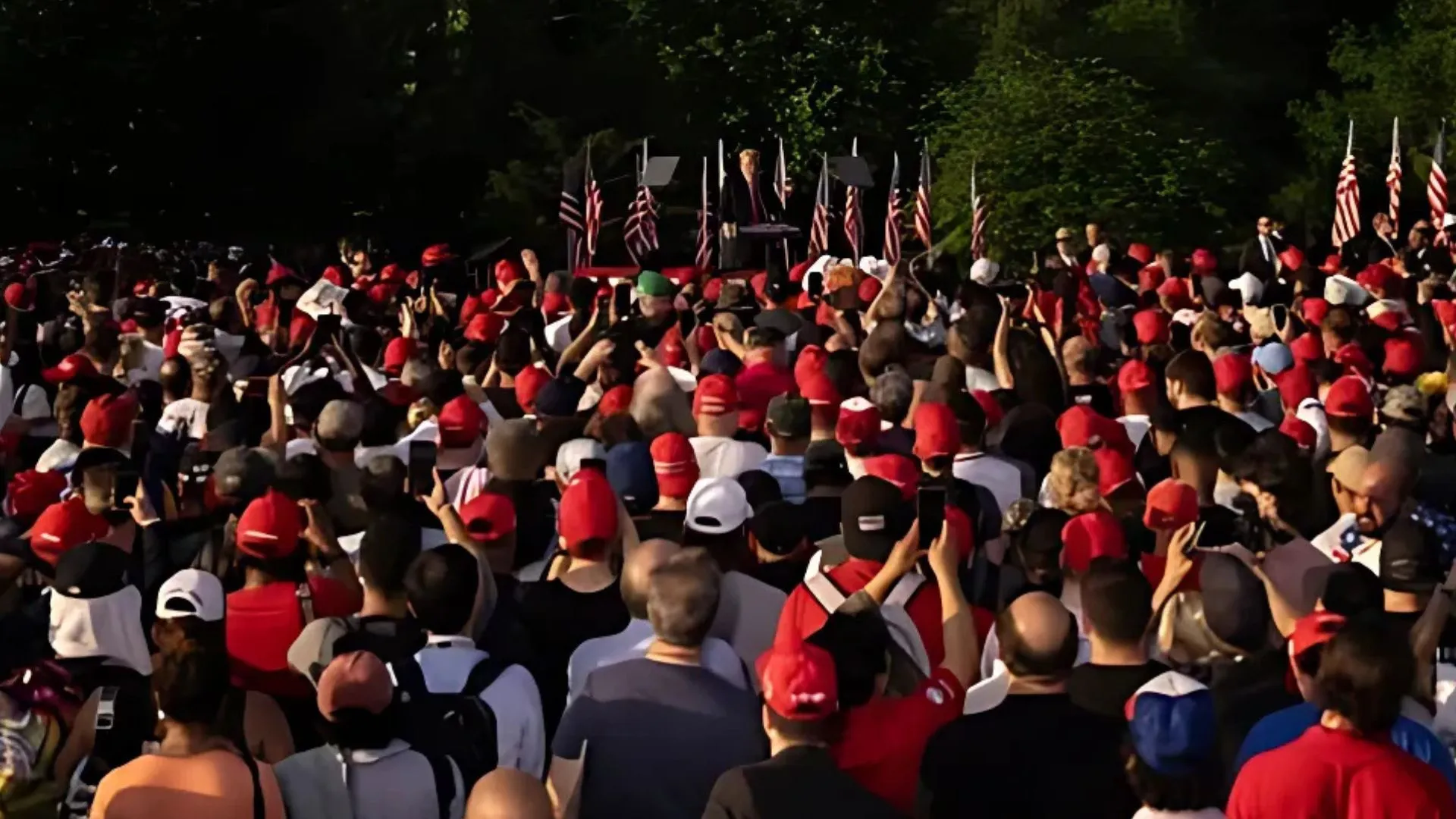
On Sunday, Donald Trump held a rally at Madison Square Garden in New York, a strategic choice in a state that has leaned Democratic since Ronald Reagan’s 1984 victory. Trump aimed to showcase his reach within a traditionally “Blue America.” However, the event was marred by controversial remarks from comedian Tony Hinchcliffe, whose comments about Puerto Rico sparked backlash, even among fellow Republicans.
Hinchcliffe’s quip about a “floating island of garbage” drew mixed reactions, highlighting the delicate nature of Trump’s appeal to minority voters. Florida Senator Rick Scott and Representative Maria Elvira Salazar both condemned Hinchcliffe’s remarks, emphasizing the need for the Republican Party to uphold values that resonate with diverse communities.
The Growing Influence Of Latino Voters
Latino voters are increasingly emerging as a key demographic in this election cycle. As the second-largest group of eligible voters in the U.S. with 36.2 million individuals, their political leanings could significantly impact the outcome. Recent polling indicates a notable shift in support, with 56% favoring Harris and 39% supporting Trump, compared to Joe Biden’s 59% support in 2020 and Hillary Clinton’s 66% in 2016.
Mark Hugo Lopez, director of race and ethnicity research at Pew, notes that the evolving identity of Latino voters—many of whom are now multigenerational Americans—has influenced their political preferences. Economic issues, particularly rising housing costs and inflation, have driven many to align with Republican messaging, making their support vital for both parties.
Asian-American Voter Trends
Similarly, Asian-American voters, historically leaning Democratic, are showing signs of shifting allegiance. From 2016 to 2024, the proportion identifying with the Republican Party rose from 15% to 22%, according to AAPI Data. However, Democratic support has also fluctuated, with 42% identifying as Democratic, 22% as Republican, and 27% as independent.
This demographic, now comprising about 6% of the electorate, is significant, with an estimated 15 million eligible voters. Notably, support for the Republican Party among Chinese-Americans doubled from 8% to 16% between 2016 and 2024, while Indian-American support increased from 8% to 21%. However, experts caution against overgeneralizing these trends due to varying sample sizes and margins of error in surveys.
The Challenge Of Engaging Black Voters
Black voters have long been a cornerstone of the Democratic Party, yet there are signs of discontent, particularly among young Black men. Pew Research indicates that while 92% of Black voters supported Biden in 2020, only 78% support Harris currently. Economic issues dominate their concerns, with many prioritizing jobs and financial stability over party loyalty.
Former President Barack Obama’s recent rally in Pittsburgh sought to address this disengagement, noting a lack of enthusiasm, especially among Black men. His comments hinted at deeper issues regarding perceptions of Harris as a leader. Despite the challenges, experts caution that polling may not fully capture the complexities of Black voter sentiment.
What Lies Ahead
As the election approaches, the interplay of these demographic shifts will play a critical role in determining the outcome. For Harris, securing the support of minority voters is essential to bolster her campaign. Meanwhile, Trump aims to capitalize on the changing landscape by appealing to those who feel disillusioned with the Democratic Party.
MUST READ | Donald Trump Loses His Cool At Rally, Mimics Sexual Act After Mic Failure | WATCH